陳韻如 博士
|
基因體研究中心助研究員 |
![]()
| 起訖時間 | 職稱 | 服務機關 |
| 2003 | 博士 | 美國北卡州立大學 |
| 2004-2006 | 博士後 | 美國加州大學爾灣分校 |
| 2006-2007 | 博士後 | 中央研究院基因體研究中心 |
| 2007-至今 | 助研究員 | 中央研究院基因體研究中心 |
研究方向
蛋白質錯誤摺疊及類澱粉蛋白疾病致病機轉
我們的研究重點在於運用多種生物化學、生物物理、及分子細胞學的技術,來了解蛋白質錯誤摺疊之類澱粉沉積症的致病機轉。類澱粉沉積症多與神經退化疾病相關,其中阿茲海默症為本世紀全球及臺灣日趨嚴重的疾病。類澱粉蛋白是由錯誤摺疊的蛋白質堆積,而形成擁有專一乙級結構的纖維。類澱粉蛋白的堆積會形成許多不同的形狀物,而對神經細胞有毒害。很有趣的是,許多有著不同一級氨基酸序列的類澱粉蛋白,也有著共同的形狀物,這暗示著它們享有共同的堆積機制及相關毒性。我們將從了解致病蛋白堆積物的功能及機制,進而發展其偵測方式、有效抗體、及小分子抑制物。同時,我們亦研究與類澱粉蛋白相關的醣分子、前驅物、及調節物之結構、功能、與交互作用。我們希望能提供這些神經退化疾病早期診斷與治療的新方向。目前我們的研究著重於下列類澱粉及似類澱粉蛋白及其作用分子:(1)阿茲海默症病人腦部老年斑塊的主要組成:類澱粉乙形蛋白(amyloid-β)、(2)帕金森氏症病人腦部路易士體的主要組成α-synuclein、及(3)額顳葉失憶/肌萎縮側索硬化症中病癥的TDP-43蛋白。我們主要的研究目標如下:
- 蛋白質在神經退化疾病中的摺疊與錯誤摺疊機制
- 類澱粉蛋白多倍體化及在神經退化疾病中引發之毒性機制
- 蛋白質、醣類、及脂質與病理相關蛋白在神經退化疾病中的其相互作用
- 針對神經退化疾病發展藥物篩選、診斷及治療策略
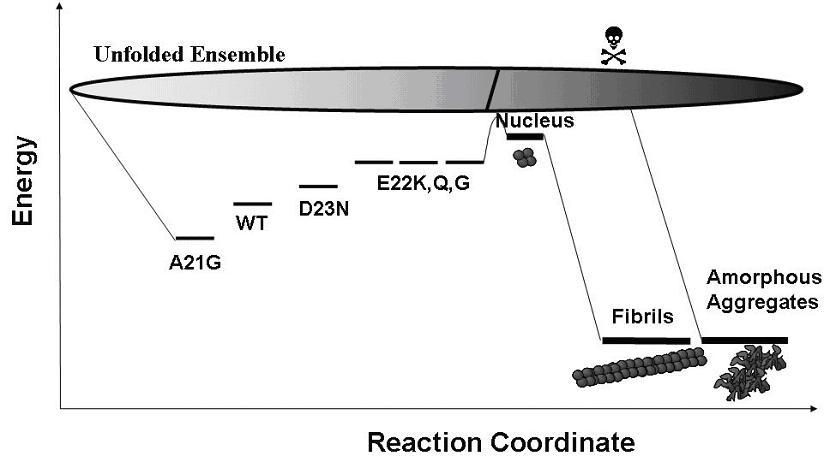
Schematic free-energy landscape for folding and aggregation mechanisms of amyloid-beta and the familial mutants.
The folding stability of Abeta variants predominantly determine the kinetics of nucleation in the fibrillization process. The less stable species can cross the activation barrier easier toward the pathological states.
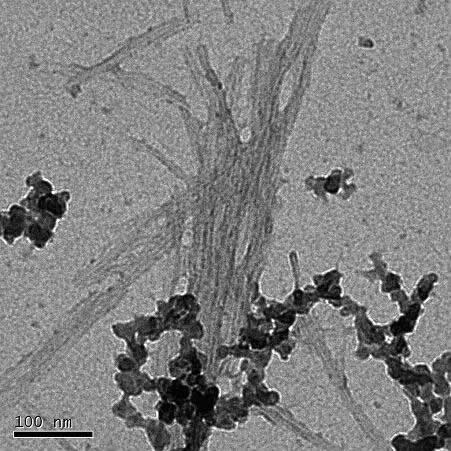
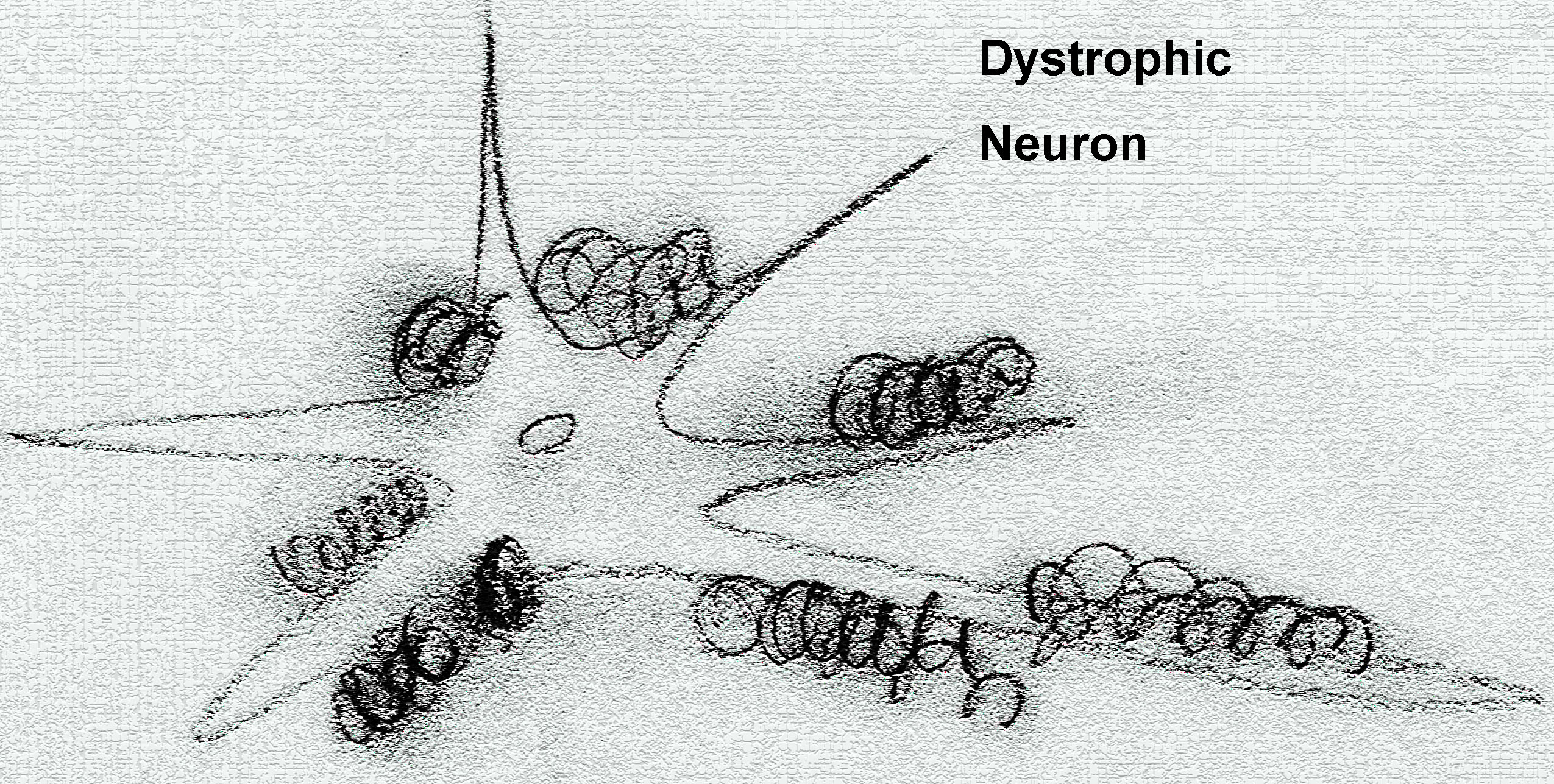
A transmission electron microscope image of amyloid β fibrils.
The different amyloid aggregates cause different cytotoxicity.
研究著作
- Huei-Jyuan Pan, Ruei-Lin Wang, Jian-Long Xiao, Yu-Jen Chang, Ji-Yen Cheng, Yun-Ru Chen, and Chau-Hwang Lee*. Using optical profilometry to characterize cell membrane roughness influenced by Amyloid-beta peptide and electric fields. (Jan, 2014) Journal of Biomedical Optics, 19 (1):011009.
- Man Hoang Viet, Chun-Yu Chen, Chin-Kun Hu, Yun-Ru Chen*, and Mai Suan Li*. Discovery of Dihydrochalcone as a potential lead for Alzheimer’s disease: in silico and in vitro study. (Nov., 2013) PLoS One, 8(11):e79151. (*co-corresponding author)
- Wei-Chieh Cheng*, Chen-Yi Weng, Wen-Yi Yun, Shang-Yu Chang, Yu-Chun Lin, Fuu-Jen Tsai, Fu-Yung Huang, Yun-Ru Chen. Rapid modifications of N-substitution in iminosugars: Development of new β-glucocerebrosidase inhibitors and pharmacological chaperones for Gaucher disease. (Sep., 2013) Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 1, 5021-5028
- Rong-Jie Chen, Wei-Wei Chang, Yu-Chun Lin, Pei-Lin Cheng, and Yun-Ru Chen*. Alzheimer’s Amyloid-β Oliogmers Rescue Cellular Prion Protein Induced Tau Reduction via Fyn pathways. (*corresponding author). (Sep., 2013) ACS Chemical Neuroscience, 4(9):1287-96.
- Yi-Ting Wang, Pan-Hsien Kuo, Chien-Hao Chiang, Jhe-Ruei Liang, Yun-Ru Chen, Shuying Wang, James C. K. Shen, and Hanna S. Yuan. The truncated C-terminal RRM domain of TDP-43 plays a key role in forming proteinaceous aggregates. J Biol. Chem., 288 (13), 9049-57 (2013)
- Winny Ariesandi, Chi-Fon Chang, Tseng-Erh Chen, and Yun-Ru Chen*. Temperature-dependent structural changes of Parkinson's alpha-synuclein reveal the role of pre-existing oligomers in alpha-synuclein fibrillization. (*corresponding author). PLoS One., 8(1):e53487 (2013).
- Yi-Hung Liao, Yu-Jen Chang, Yuji Yoshiike, Yu-Chorng Chang*, and Yun-Ru Chen*. Negatively charged gold nanoparticles inhibit Alzheimer’s amyloid-b fibrillization, induce fibril dissociation, and mitigate neurotoxicity (*co-corresponding author). Small, 8, 23, 3631-3639 (2012).
- Wei-Ting Chen, Chen-Jee Hong, Ya-Tzu Lin, Wen-Han Chang, He-Ting Huang, Jhih-Ying Liao, Yu-Jen Chang, Yi-Fang Hsieh, Chih-Ya Cheng, Hsiu-Chih Liu, Yun-Ru Chen*, and Irene H Cheng *. Amyloid-beta (Ab) D7H mutation increases oligomeric Ab42 and alters properties of Ab-zinc/copper assemblies (*co-corresponding author) PLoS One., 7(4): e35807 (2012).
- Wei-Ting Chen, Yi-Hung Liao, Hui-Ming Yu, Irene Cheng, and Yun-Ru Chen*. Distinct Effects of Zn2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, and Al3+ on Amyloid-b Stability, Oligomerization, and Aggregation: Amyloid-b Destabilization Promotes Annular Protofibril Formation. (*corresponding author) J Biol. Chem., 286 (11), 9646-56 (2011).
- Chun-Lun Ni, Hoi-Ping Shi, Hui-Ming Yu, Yun-Chorng Chang, and Yun-Ru Chen*. Folding Stability of Amyloid-b40 Monomer is an Important Determinant of the Nucleation Kinetics in Fibrillization (*corresponding author) FASEB J., 25(4), 1390-401 (2011). (featured as a key scientific article in Global Medical Discovery)